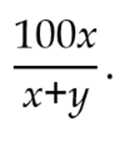ตำรายาของประเทศไทย
Thai Pharmacopoeia
สำนักยาและวัตถุเสพติด กรมวิทยาศาสตร์การแพทย์ กระทรวงสาธารณสุข
Bureau of Drug and Narcotic, Department of Medical Sciences, Ministry of Public HealthThai name เปลือกซินโคนา (PLUEAK CINCHONA)
Category Antimalarial and bitter.
Cinchona Bark consists of the dried bark of Cinchona pubescens Vahl (C. succirubra Pav. ex Klotzsch), or of its varieties or its hybrids (Family Rubiaceae). It contains not less than 6.5 per cent of total alkaloids, of which 30 to 60 per cent are alkaloids of the quinine-type, calculated on the dried basis.
Origin of plant Cinchona is native to Central America and South America, but hybrids are cultivated in India, Africa and the Far East.
Constituents Cinchona Bark contains the quinine-type alkaloids, of which quinine and quinidine are its major components. It also contains the cinchonine-type alkaloids, quinic acid and quinovose.
Description Odour, mild, characteristic; taste, intensely bitter and somewhat astringent.
Macroscopical Quilled or curved pieces of dried stems or barks, 2 to 6 mm thick; externally usually rough with transverse fissures and longitudinal furrows or wrinkles, dull brownish grey or grey and frequently with lichens; some varieties experience exfoliation of the outer surface; internally deep reddish brown and striated; the external fracture is short and the inner fracture is fibrous.
Microscopical Transverse section of the cork shows thin-walled cells with red brown contents, cortex, phloem, medullary rays, and sclereids. Cortex, narrow, consisting of tangentially elongated pitted cells containing starch granules or amorphous red-brown matter, with scattered idioblasts containing microprisms of calcium oxalate and large secretory cells. Phloem: narrow sieve tubes, transverse sieve plates and phloem parenchyma, and large characteristic spindle-shaped phloem fibres occurring in isolation or in irregular radial rows. Medullary rays, thin-walled, elongated cells radially arranged. Sclereids, very rare.
Powdered drug of Cinchona Bark possesses the microscopical characteristic of the unground drug. Starch granules, mostly simple but occasionally with 2 or 3 components, free or included in parenchyma cells.
Other relevant information
1. It is contra-indicated in pregnant women.
2. It is incompatible with iodides and salicylates.
Packaging and storage Cinchona Bark shall be kept in well-closed containers, protected from light, and stored in a dry place.
Identification
A. Shake 100 mg for 1 minute with 5 mL of 1 M sulfuric acid and filter. To 1 mL of the filtrate add 0.2 mL of mercuric-potassium iodide TS. A precipitate is formed. Dilute the remainder of the filtrate to 10 mL with water. The resulting solution, when examined under ultraviolet light (366 nm) shows a blue fluorescence, which disappears on the addition of hydrochloric acid.
B. Carry out the test as described in the “Thin-Layer Chromatography” (Appendix 3.1).
Standard solution Dissolve 17.5 mg of quinine, 2.5 mg of quinidine, 10 mg of cinchonine and 10 mg of cinchonidine in 5 mL of anhydrous ethanol.
Test solution To 100 mg, in fine powder, add 0.1 mL of strong ammonia solution and 5 mL of dichloromethane, shake for 30 minutes and filter. Evaporate the filtrate to dryness on water-bath and dissolve the residue in 1 mL of anhydrous ethanol.
Adsorbent Silica gel G, use a typical plate (20×20 cm).
Mobile phase Diethylamine, ethyl acetate, and toluene (10:20:70).
Application Apply 10 µL each of Standard solution and Test solution as 10-mm bands.
Development and drying Twice over the distance of 15 cm. Dry the developed plate at 105°, and then allow to cool.
Detection A Spray the plate with anhydrous formic acid, allow to dry in air and examine under ultraviolet light (366 nm).
Results A When examined under ultraviolet light (366 nm), the test solution shows a blue fluorescent band due to quinine in the lower third and a blue fluorescent band due to quinidine around the middle of the chromatogram, corresponding in colour and Rf to the bands shown by the standard solution.
Detection B Spray the plate with iodoplatinate TS.
Results B The test solution shows a violet band that becomes violet grey due to quinine in the lower third, an intense dark blue band, and two violet bands that becomes violet grey due to cinchonidine, quinidine and cinchonine, respectively around the middle of the chromatogram, corresponding in colour and Rf to the bands shown by the standard solution.
Loss on drying Not more than 10.0 per cent w/w after drying at 105° for 2 hours (Appendix 4.15).
Foreign matter Not more than 2.0 per cent w/w (Appendix 7.2).
Total ash Not more than 6.0 per cent w/w (Appendix 7.7).
Assay
Standard quinine preparation Dissolve about 30 mg of quinine, accurately weighed, in 0.1 M hydrochloric acid and dilute to 1000.0 mL with 0.1 M hydrochloric acid.
Standard cinchonine preparation Dissolve about 30 mg of cinchonine, accurately weighed, in 0.1 M hydrochloric acid and dilute to 1000.0 mL with 0.1 M hydrochloric acid.
Assay preparation Mix about 1 g, in fine powder and accurately weighed, with 10 mL of water and 7 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid in a 250 mL conical flask. Heat in a water-bath for 30 minutes, allow to cool. Add 25 mL of dichloromethane, 50 mL of ether and 5 mL of a 20 per cent w/v solution of sodium hydroxide. Shake for 30 minutes and add 3 g of tragacanth and shake until the mixture becomes clear. Filter through a plug of absorbent cotton and rinse the flask with five 20-mL portions of a mixture of 1 volume of dichloromethane and 2 volumes of ether. Combine the filtrate and washings, evaporate the filtrate to dryness and dissolve the residue in 10.0 mL of anhydrous ethanol. Evaporate 5.0 mL of this solution to dryness, dissolve the residue in 0.1 M hydrochloric acid and dilute to 1000.0 mL with 0.1 M hydrochloric acid.
Procedure Measure the absorbances of Standard quinine preparation, Standard cinchonine preparation and Assay preparation at the maximum at about 316 nm and 348 nm, using 0.1 M hydrochloric acid as the blank (Appendix 2.2).
Calculation Calculate the percentage content of alkaloids, in the portion of Cinchona Bark taken by the expression:

where x = percentage content of quinine-type alkaloids,
y = percentage content of cinchonine-type alkaloids,
w = the weight, in g, of Cinchona Bark in Assay preparation,
A316 and A348 = the absorbances of Assay preparation at 316 and 348 nm, respectively, A316q and A348q = the absorbances of Standard quinine preparation at 316 and 348 nm, respectively, corrected to a concentration of 1 µg per mL,
A316c and A348c = the absorbances of Standard cinchonine preparation at 316 and 348 nm, respectively, corrected to a concentration of 1 µg per mL.
Calculate the content, of total alkaloids (x+y), and calculate the relative content of quinine-type alkaloids, using the expression: